May 23, 21 · RR = risk ratio;Pref = Prevalence of the outcome in the reference group oddsratio Share Cite Improve this question Follow asked mins ago Explaining Odds Ratio and Relative Risk to the statistically challenged 2 Fisher's Exact Test, Relative Risk or Odds RatioOR = odds ratio;

Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk
Odds ratio or relative risk for cross-sectional data
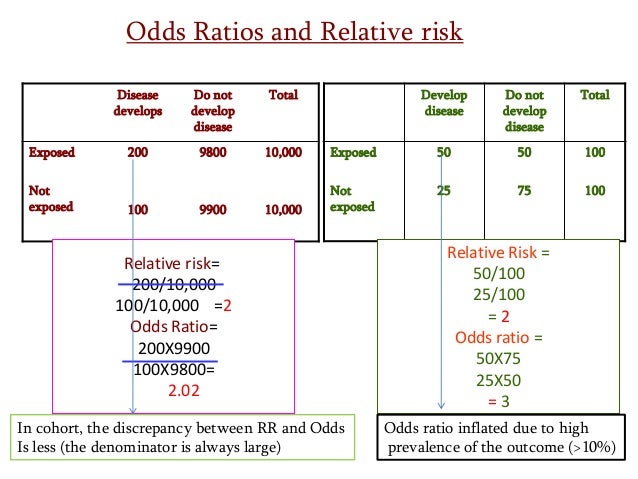
Odds ratio or relative risk for cross-sectional data-When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Dec 30, 16 · Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedFeb 07, 14 · It has been proposed that the sample odds ratio is a good estimate of the population relative risk and can be interpreted as a relative risk when the disease or outcome is rare in the population, typically when the prevalence is less than 10%Odds Ratio and Relative Risk are examined in epidemiological context Odds ratio can mislead if a "Common Event" is studied, since it can exaggerate effects
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalAug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while aMay 15, 14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio May 15, 14 • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regret
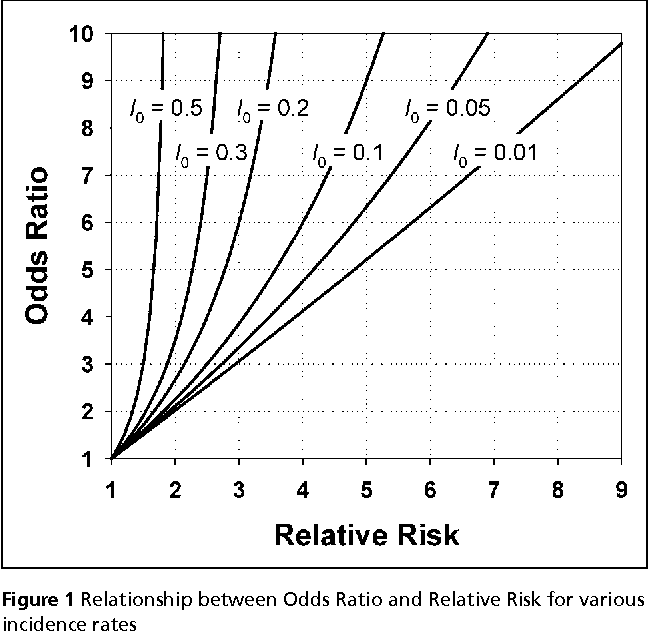
Aug 16, 18 · For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);Portantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) And it is this fact that enables us, most of the time, to approximate the relative risk with the odds ratio Table 5 below illustrates the relationship between RR and OR for some probabilities of the outcomeJul 11, 16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Jun 01, 09 · Risk is based on proportion of persons with disease = cumulative incidence Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk Since all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each typeOdds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiertThe relative risk is mistaken by some with the odds ratio and absolute risk Relative risk is the ratio of the probability of an event occurring with an exposure versus the probability of the event occurring without the exposure Thus to calculate the relative risk, we must know the exposure status of all individuals (either exposed or not



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated


1 5 Nutrition Research Statistics Nutrition Flexbook
Apr 21, 21 · The ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measureJan 10, 13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionOdds Ratio versus Relative Risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good, and the odds ratio can be used


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science



Math3010 Week 6
Jan 08, 16 · Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 tableRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increaseThe odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research
Sep 02, · Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio September 2, , 500 pm The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficialOdds ratio versus relative risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be usedMar 28, 1998 · Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02)



Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
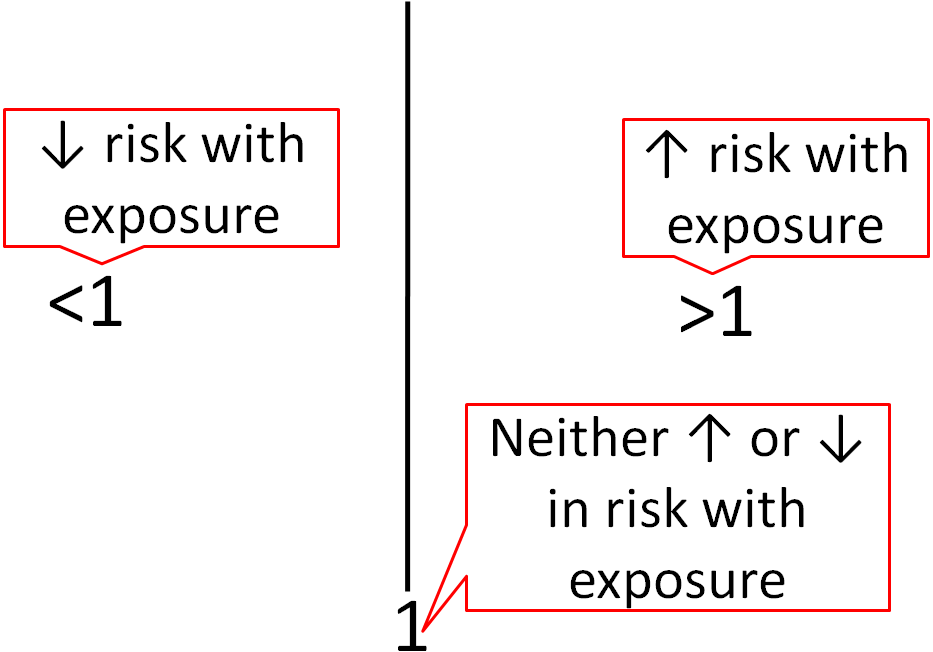
With an odds ratio, the outcome can be the starting point with which we can determine the relative odds of someone having been exposed to a risk factor Alternatively, we can also use it to describe the ratio of disease odds given the exposure statusIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Oct 01, 07 · Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
May 04, 09 · A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidenceThe relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative riskSep 16, 02 · Cases 1 and 4 have the same absolute risk reduction, NNT, and odds ratios, but very different relative risk, relative risk reduction, and risk at baseline Real Example The following example 18 is a prospective study, which compares the incidences of dyskinesia after ropinirole (ROP) or levodopa (LD) in patients with early Parkinson's disease



Epidemiology Midterm Flashcards Quizlet



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk
For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the defaultDec 14, 15 · Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk Published on December 14, 15 by Howard Herrell, MD Many great things have been written about the difference between Odds Ratios (OR) and Relative Risks (RR) Every medical student at some point has been taught the difference Yet these statistical terms are confused andThe simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variable



Risk Differences And Rate Differences


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
Odds ratio and relative riskNotice that the adjusted relative risk and adjusted odds ratio, 144 and 152, are not equal to the unadjusted or crude relative risk and odds ratio, 178 and 193 The adjustment for age produces estimates of the relative risk and odds ratio that are much closer to the stratumspecific estimates (the adjusted estimates are weighted averages ofJul 01, 17 · In medical literature, the relative risk of an outcome is often described as a risk ratio (the probability of an event occurring in an exposed group divided by the probability in a nonexposed group) Certain types of trial designs, however, report risk as an odds ratio This format is commonly expressed in cohort studies using logistic regression



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventionsMay 18, 12 · Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout


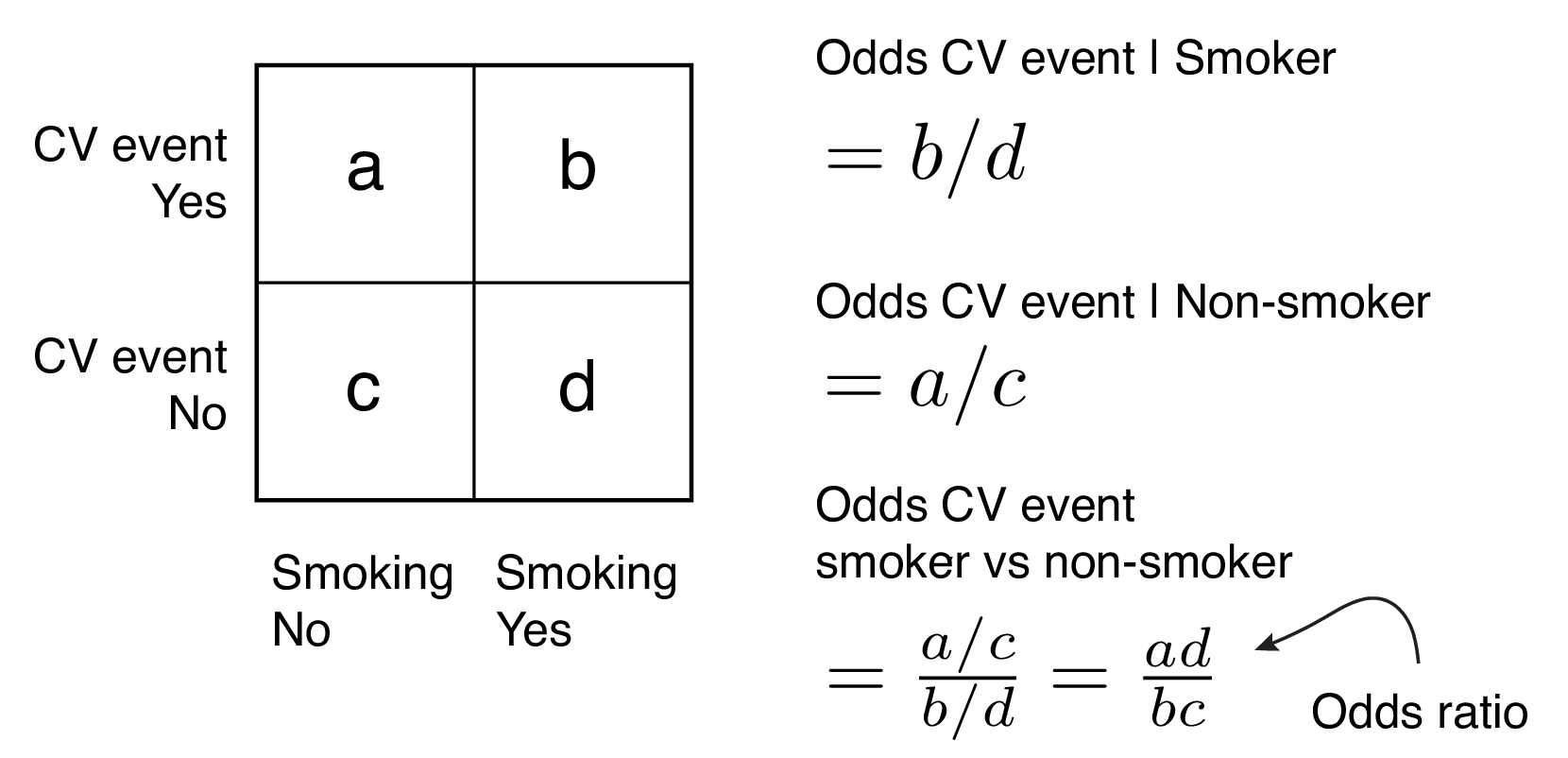
Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
The quote surely just means to say that the odds ratio is a relative risk measure rather than an estimate of the relative risk, which as already point out is only approximately the case in cohort studies/randomized trials for very low proportions By relative risk measure I mean something that is given relative to some comparison group in a way that the absolute difference depends on thePute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterIn metaanalysis for relative risk and odds ratio, studies where a=c=0 or b=d=0 are excluded from the analysis (Higgins & Thomas, 21) Literature Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research London Chapman and Hall


Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram


Epidemiology Stepwards
Feb 17, 21 · For example, a relative risk of 15 would suggest a 50% increase in risk, whereas a relative risk of 05 would suggest a 50% decrease in risk Odds ratios The main difference between this and the other two measures is that there is no way of including aOdds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Odds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to useRelative risk and odds ratio An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds ) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)



Analytical Studies



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Aug 07, 14 · If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough


Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc


Estimating Risk



Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge


Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



33 Epidemiology Ideas Cohort Study Case Control Study Study Design



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor


6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining



Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf


Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Odd Ratio Relative Risk And Attributable Risk Youtube



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056


Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08


Solved Using Relative Risk And Odds Ratio I Am Confused Chegg Com



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1



Biostatistics Flashcards Quizlet


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be


Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Odds Ratio Article



Odds Ratio Relative Risk


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Solved Present Example Of An Dolds Ratio Compared To A Re Chegg Com



Glossary Of Research Terminology



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download



Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
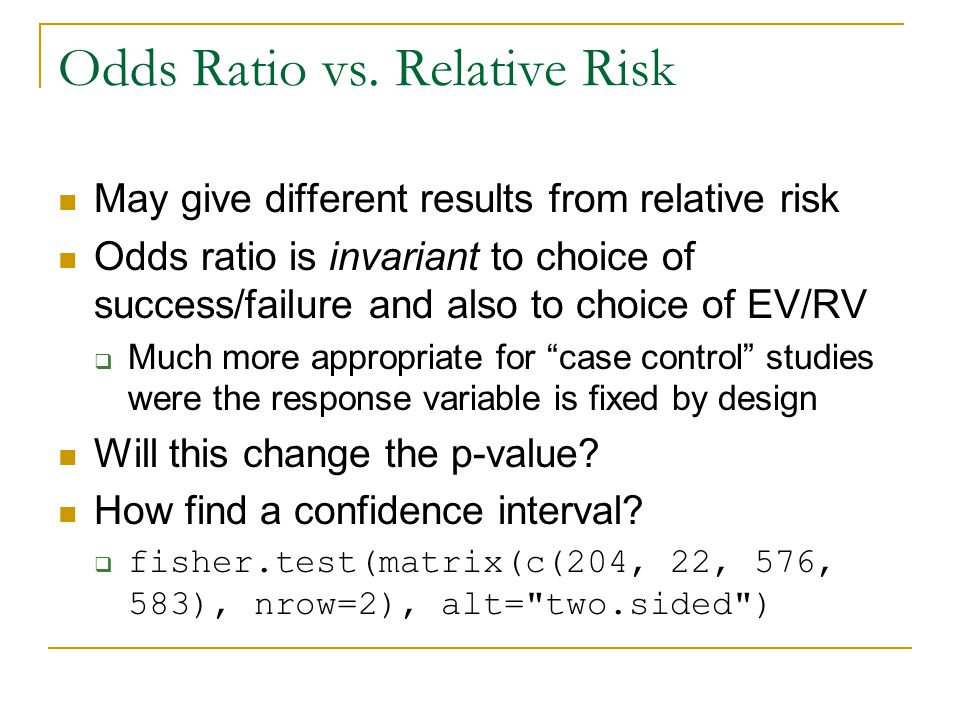


Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Relative Risk Wikipedia



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh


Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia


Relative Risk Wikipedia



Estimating Risk



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



Literature Search



Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
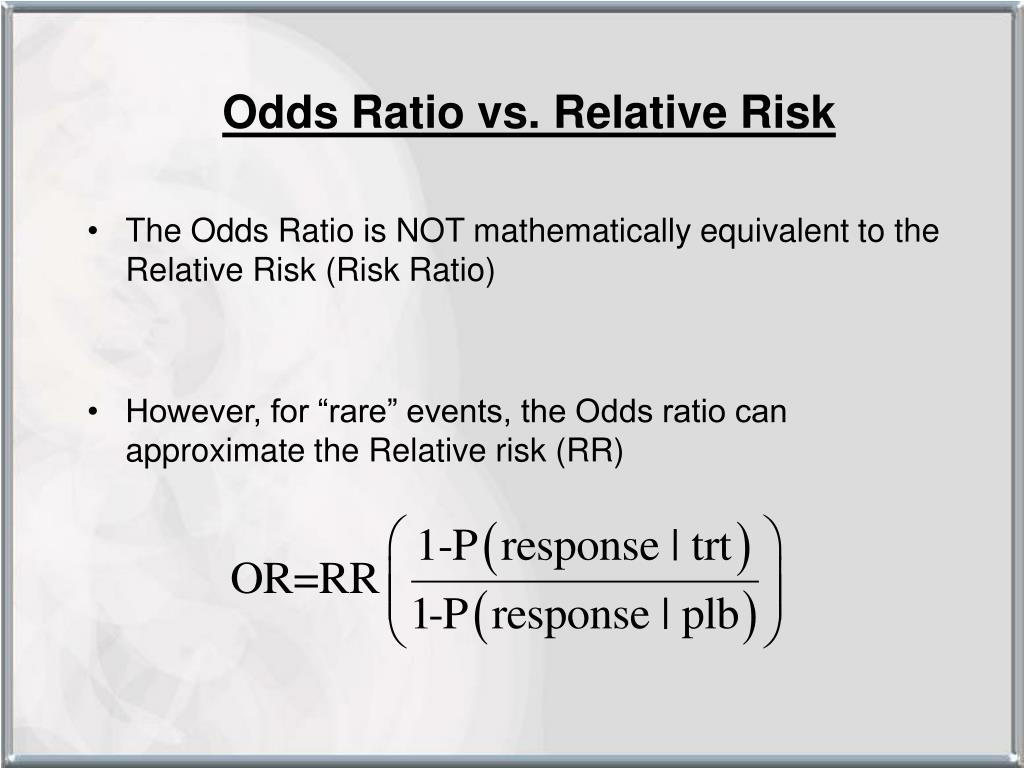


Ppt Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08 Powerpoint Presentation Id



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals


Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table


Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk And



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science



Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿